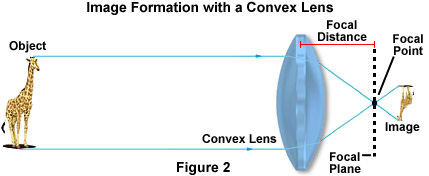
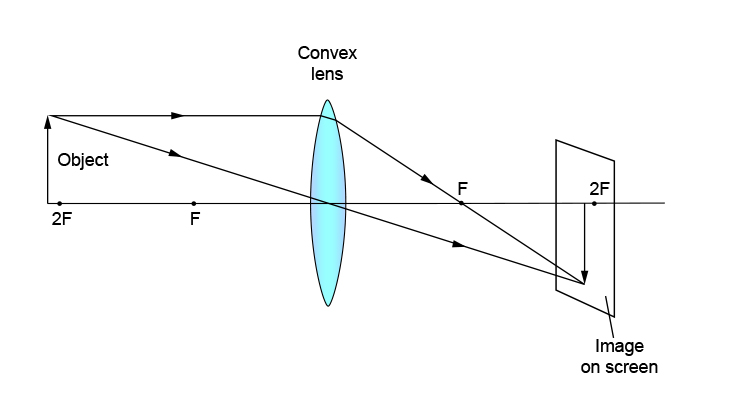
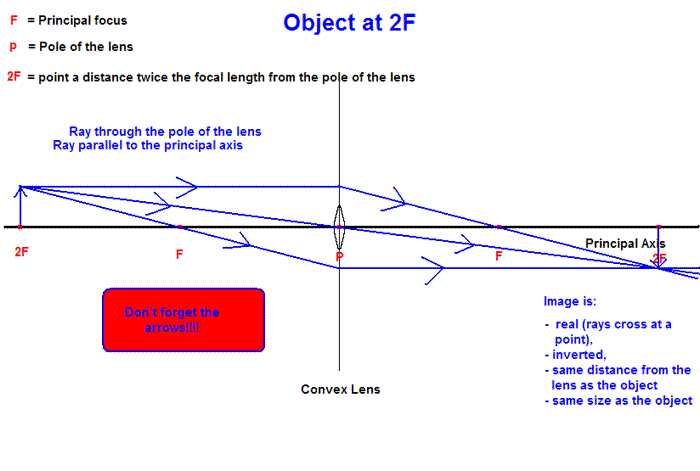
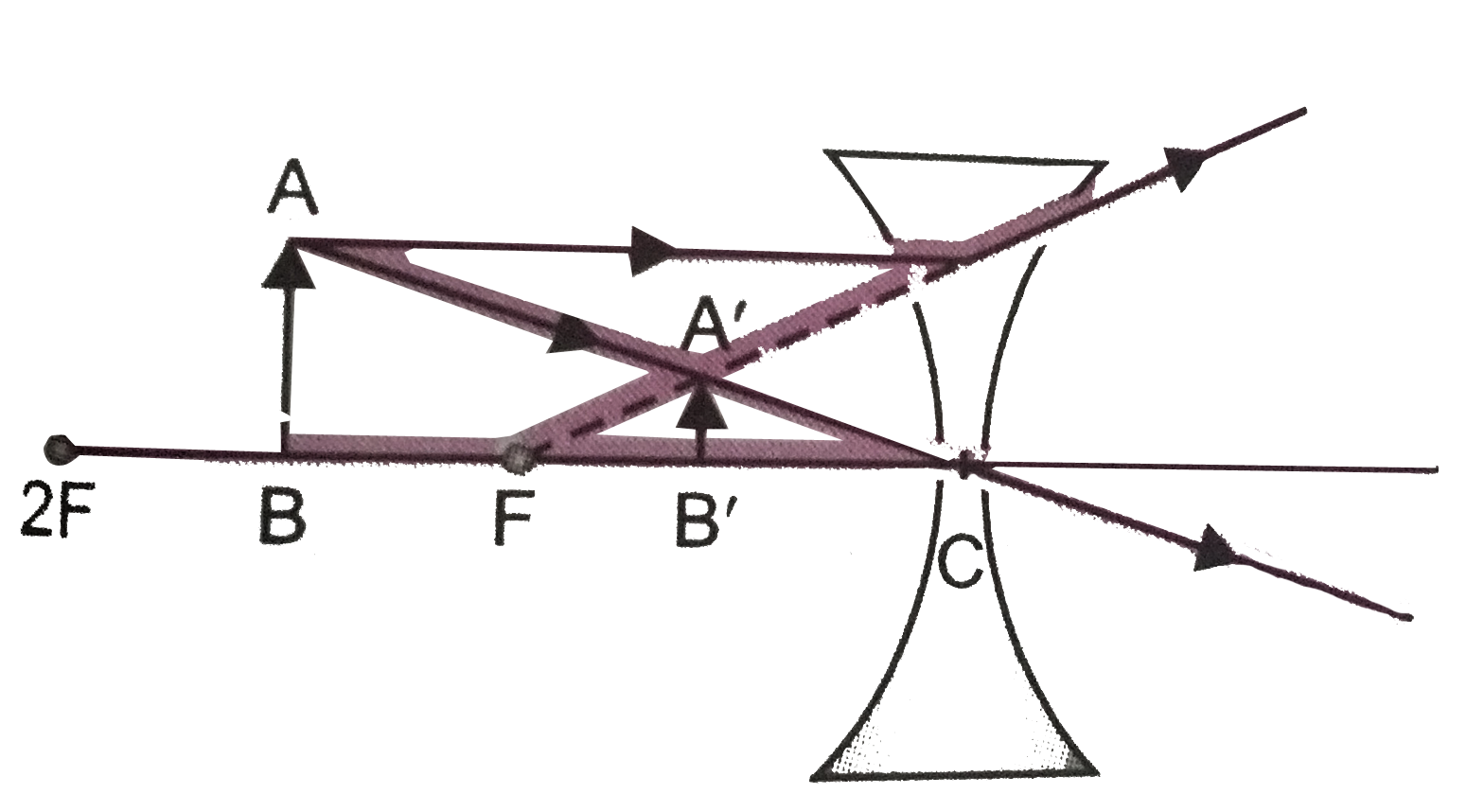
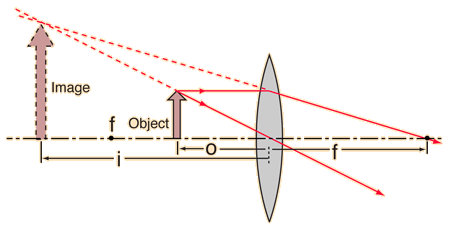
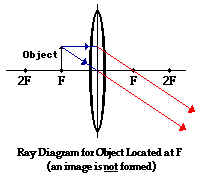
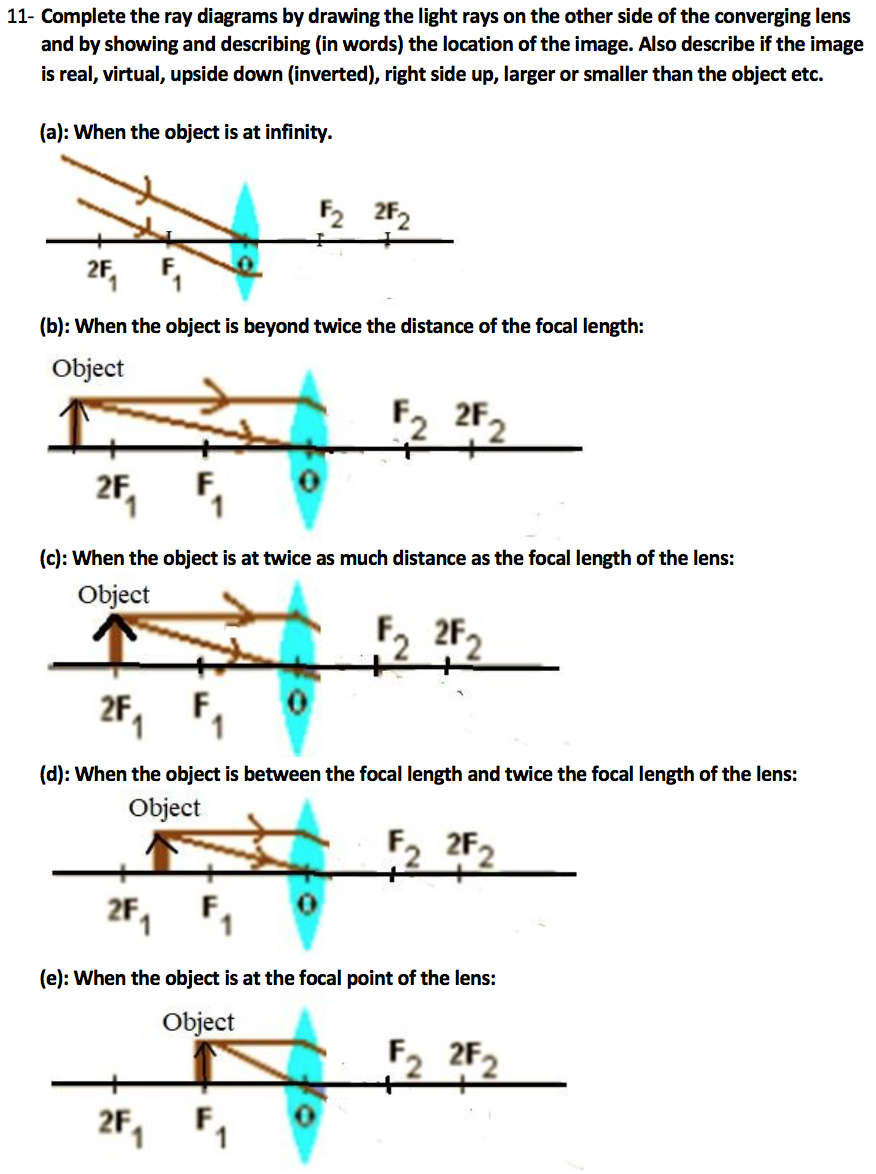
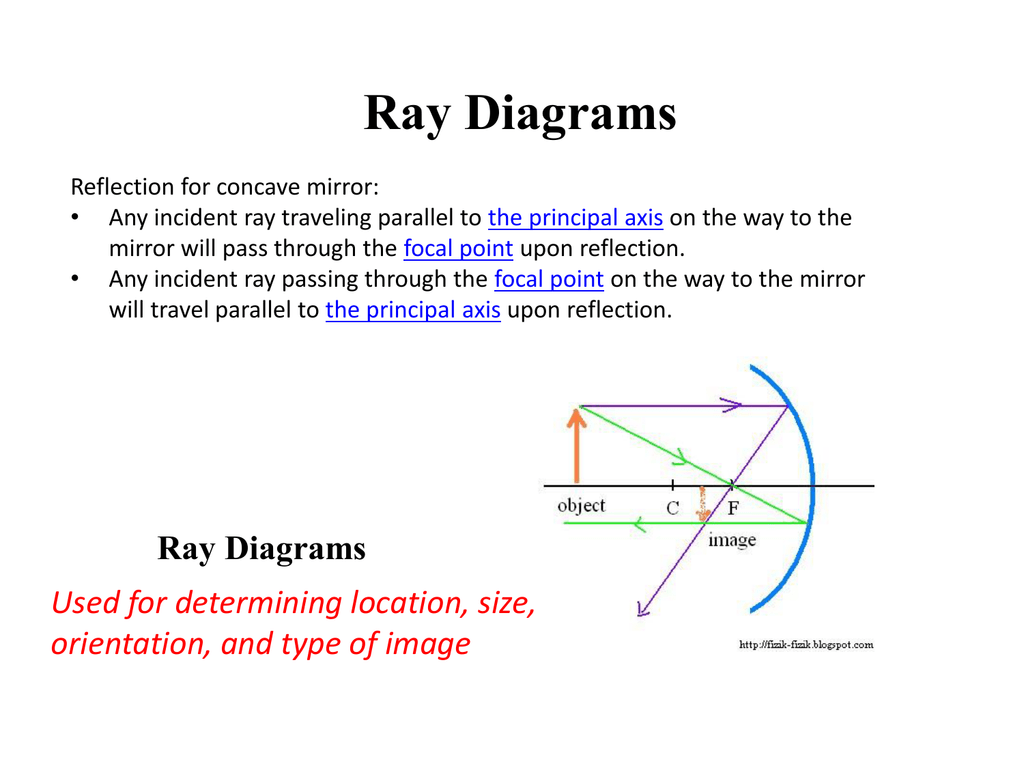
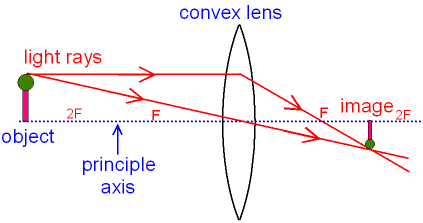
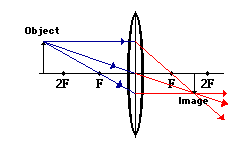
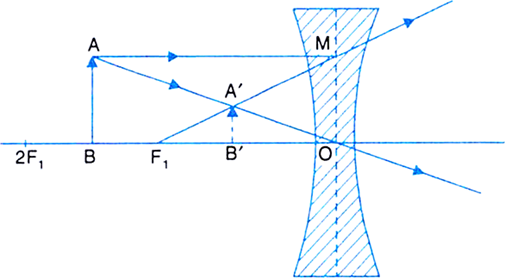
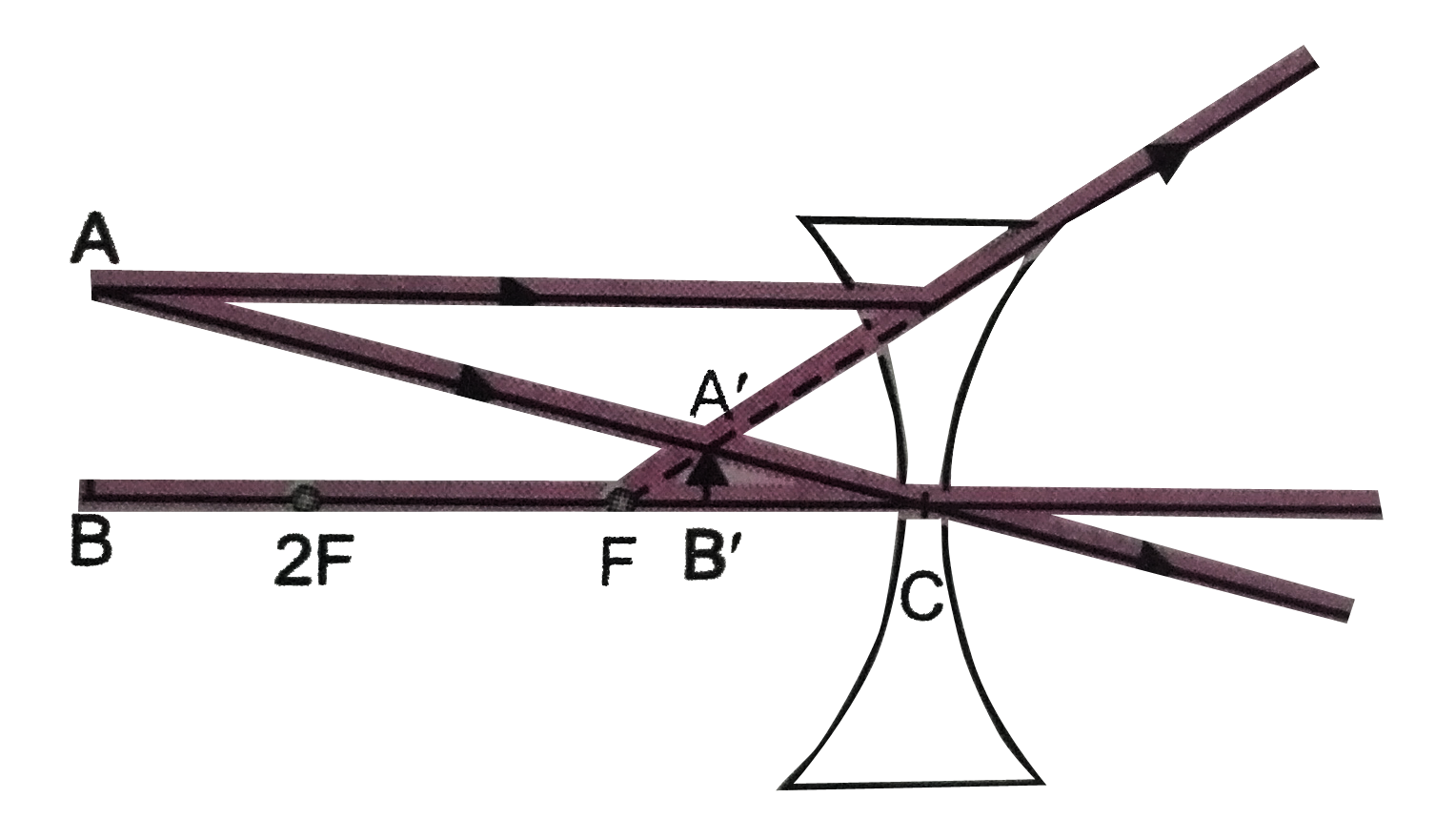
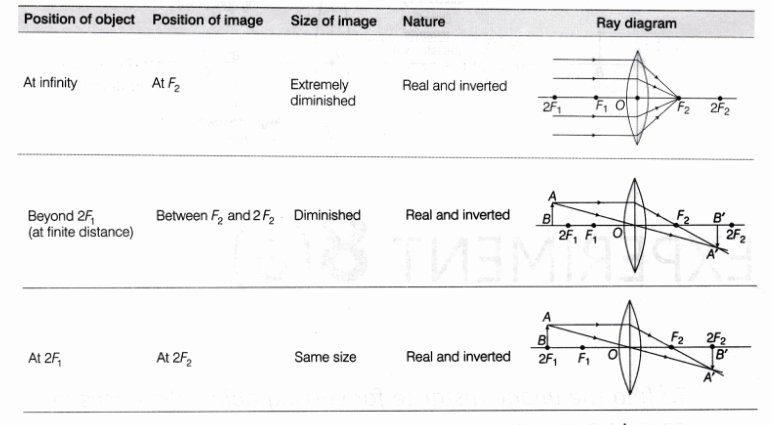
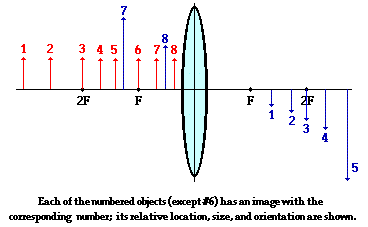
object beyond twice the focal length
The mirror and the lens are likely to be. A convex mirror has focal length of 15 cm. This schematic shows an example of a convex lens on the top and a concave lens on the bottom.
An object is placed at 20 cm from the pole of this lens.
Object beyond twice the focal length. For instance a telescope with an 80 mm wide lens and a 400 mm focal length has a focal ratio of f 5. These lines will now correspond to the positions of the points p f and c respectively. Find the focal length of the lens and the object size if the image size is 20 0cm. To the focal length of the mirror.
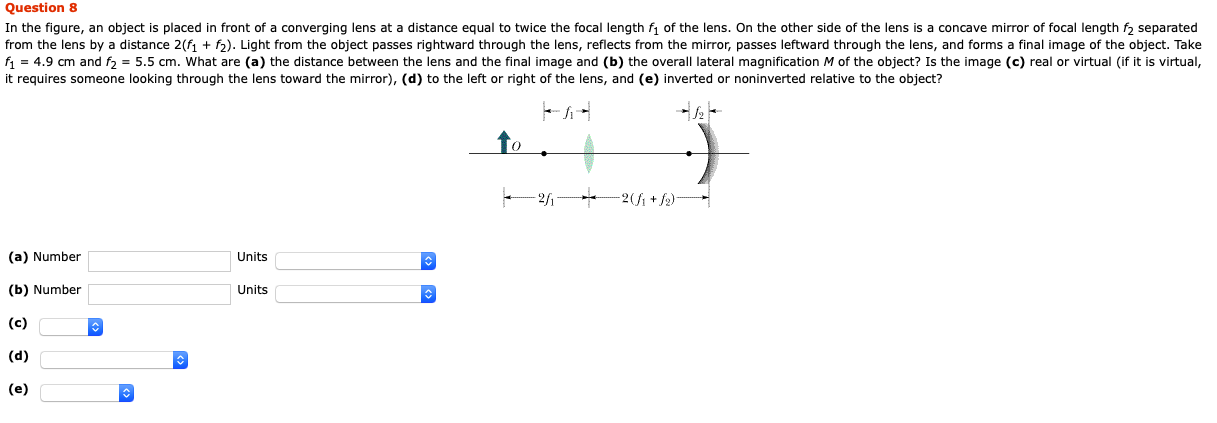
The focal length of the concave mirror in the experimental set up shown below equals. Beyond this objects under view become excessively fuzzy because. 2f 1 f 1 o f 2 2f 2. The best way to show this phenomenon is by a prism.
A 10 3 cm b 11 0 cm c 11 7 cm d 12 2 cm. When an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror the image formed is i between the focus and centre of curvature ii real and inverted and iii smaller than the object or diminished. Digital sensors are usually smaller than 35 mm film and this causes the lens to have a narrower angle of view than with 35 mm film by a constant factor for each sensor called the crop factor in everyday digital cameras the crop factor can range from around 1 professional digital slrs to 1 6 consumer slr. B at twice the focal length.
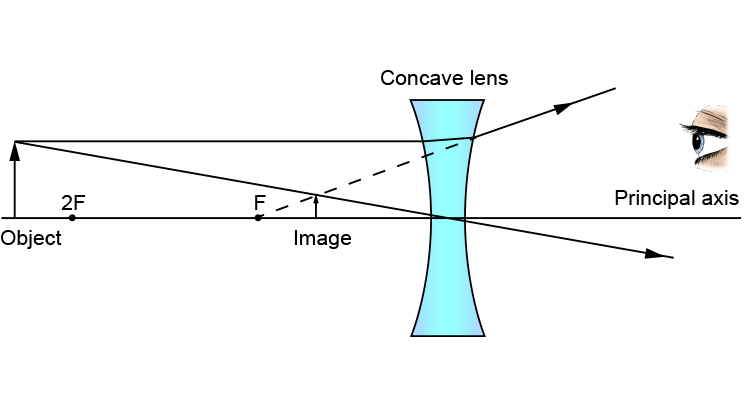
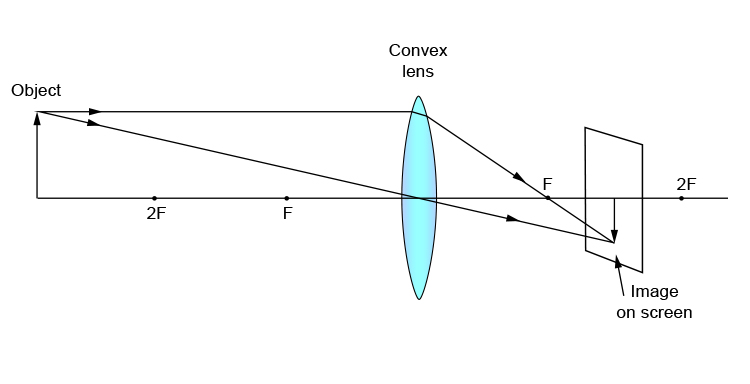
N keep a bright object say a burning candle at a position far beyond. When the object is beyond 2f 1 the image is formed between f 2 and 2f 2 it if diminished real and inverted. A camera s angle of view depends not only on the lens but also on the sensor. A at the principal focus of the lens b at twice the focal length c at infinity d between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
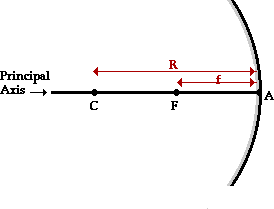
A prism refracts a light ray twice once at the entrance and once at the exit. A prism is a triangular slab of glass. It is the distance between the focus and the mirror. In a spherical mirror the radius of curvature is twice the focal.
Question 4 a spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of 15 cm. R 2f or f r. The focal point f is the point at which parallel light rays cross. Object beyond 2f d o 2f.
Focal ratio f number a lens or mirror s focal length divided by its aperture. Found to be equal to twice the focal length. Magnification limits for a standard light based microscope the maximum magnification extends up to 1 500x.